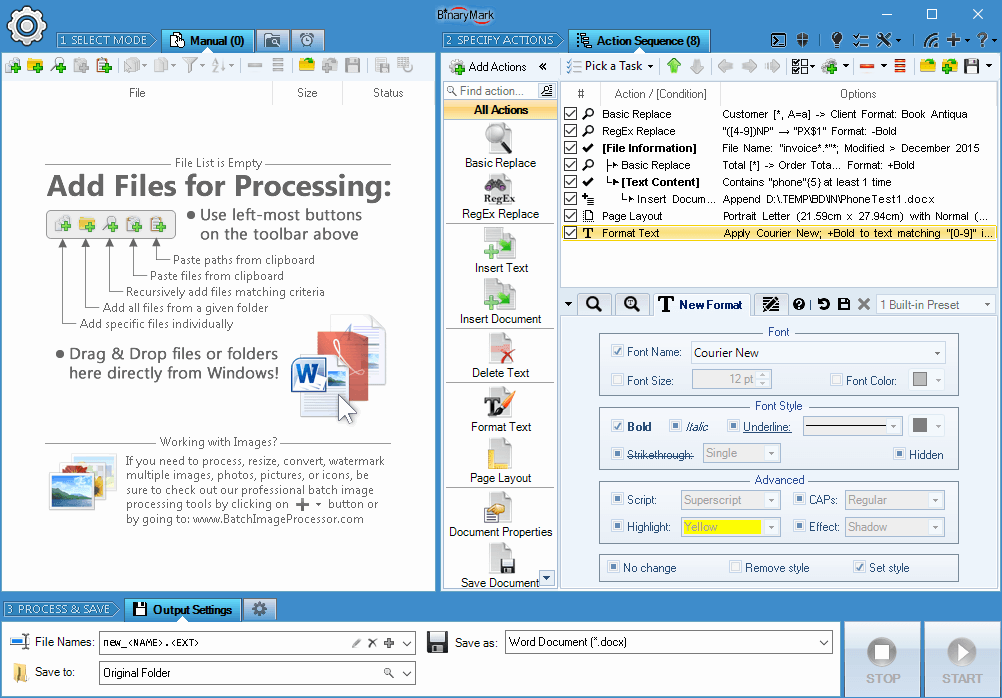
How it Works
Choose Processing Mode and Select Documents
Batch Docs can process files in 3 distinct modes:
- Manual Mode - documents are selected for processing, which is then started manually by clicking on the Start button
- Automatic / Background Mode - "monitors" are setup that scan specified folders for either existing, new, or modified documents matching criteria, which are then automatically processed once the program starts "monitoring"
- Scheduled / Triggered Mode - processing is performed by processing jobs that can run on schedule or be started on specified events
In Manual mode documents for processing can be selected and added to the processing list in multiple ways:
- One by one or in groups
- All from a given directory
- Recursive searching for files with names matching a pattern
- Recursive searching for documents with specific content. For example all documents that contain your company name.
- Drag & drop from Windows Explorer
- Paste from clipboard, paste paths
- Import from text-based file containing paths
- Right-clicking on selected documents or folder in Windows Explorer
Specify Actions to Perform
You specify which actions and operations should be performed during processing by using an Action Sequence.
Specify which actions should be performed and in what order by simply drag & dropping them.
Then you can specify various options and settings for each action to specify exactly how the action should modify your documents.
- Perform certain actions only when specific requirements are met using conditions
- Save action sequence for future use as a template
- The hierarchical structure is clearly displayed if conditions are used
- Get instant feedback about any errors
- Actions are color-coded to help you distinguish different types of actions
Step 3 - Select Output Format, Process, and Save
In the last step you choose the destination directory where processed documents will be saved; file naming pattern; document file format; and some other processing options.
- Use both relative and absolute paths when specifying output location.
- Specify very detailed file naming pattern: use file attributes, random characters, hashes, EXIF meta-data, and more!
- Adjust file dates and attributes
- Set backup and other options
When you have configured all the output options, the program can begin processing documents. As it processes documents, document list will be automatically updated reflecting detailed progress. Processing can be stopped any time.
At the end the program will display a detailed summary; a processing log will also be available so you can examine any warnings or errors if they occurred.
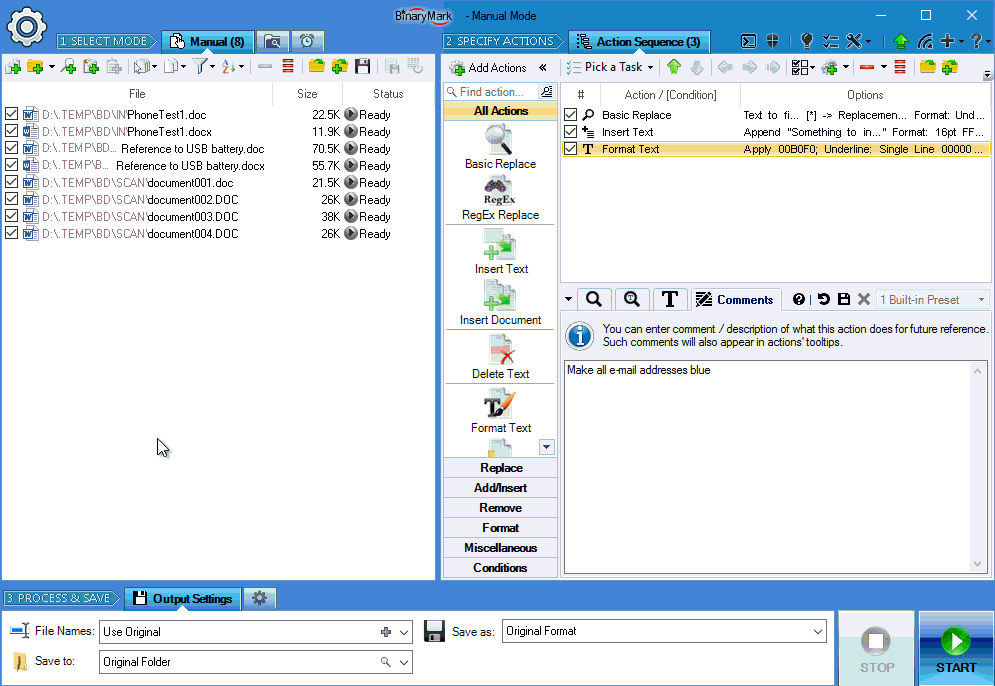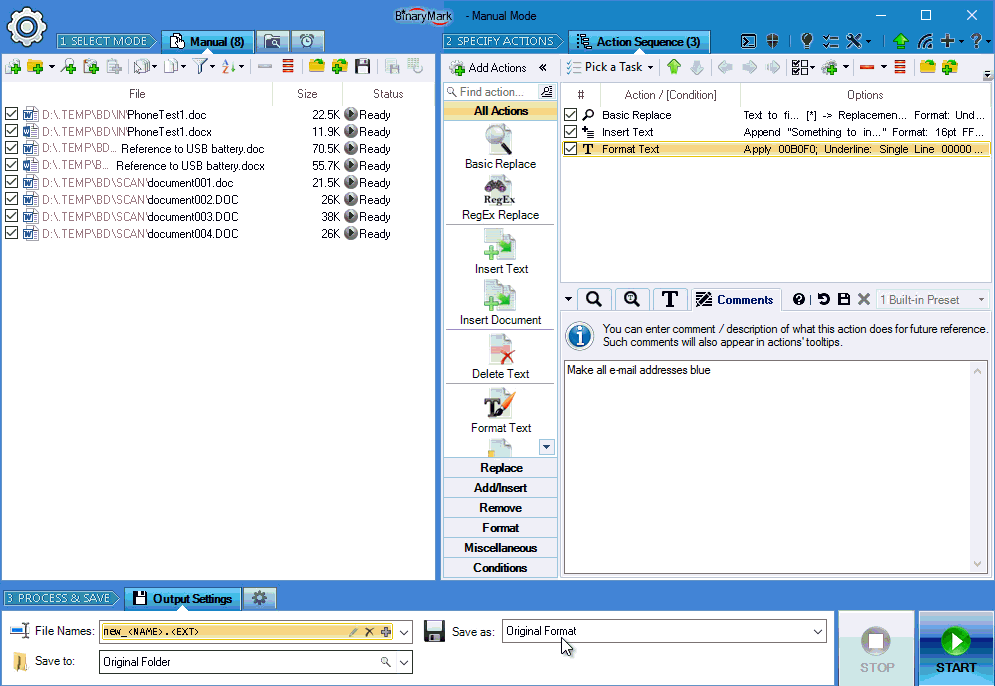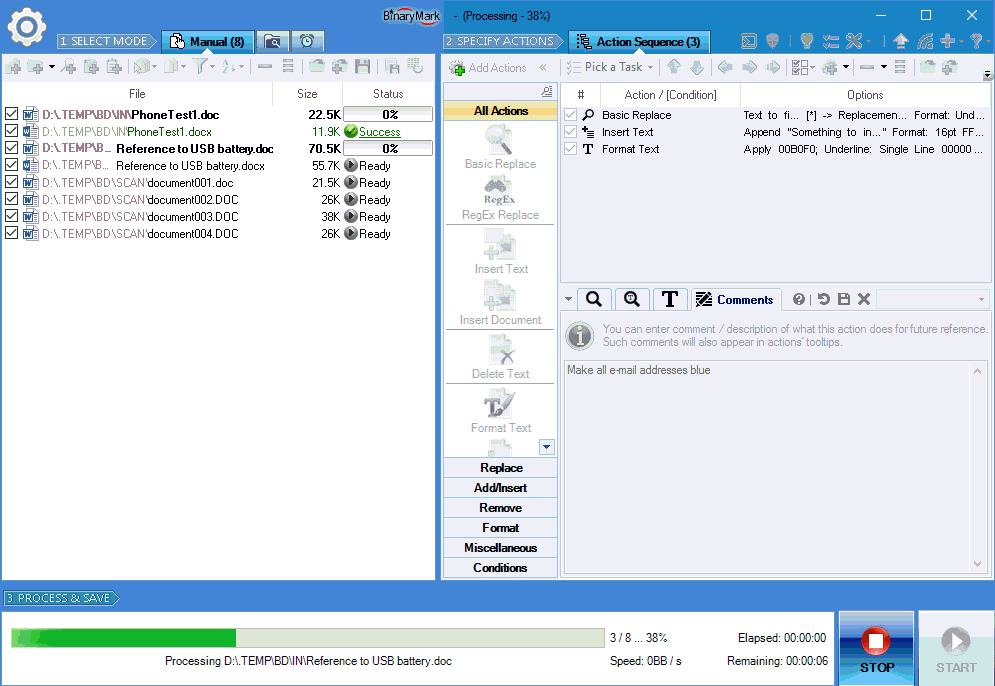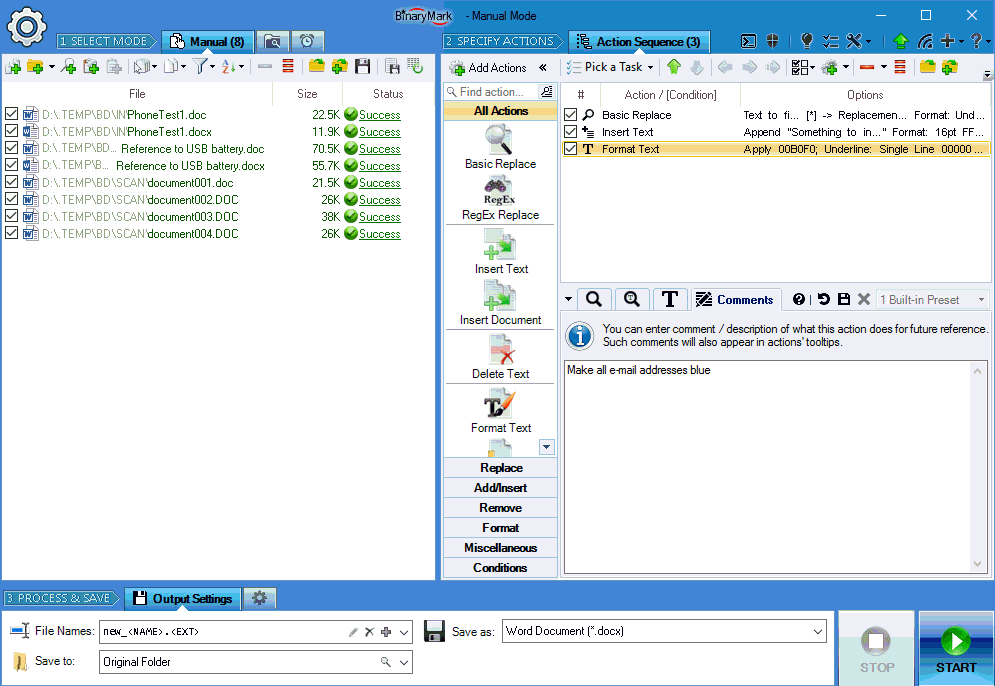
Search & Replace Text in Documents
Basic Search & Replace
- Replace characters, words, phrases, or whole sentences
- Multi-line search & replace
- Use wildcards
*in your searches - Option to ignore letter case when performing text search
- Search for special and control characters with character escapes:
\20
Use Regular Expressions
Regular Expressions allow for virtually endless possibilities when it comes to finding a specific text or a set of similar text strings. They act as patterns or blueprints and will match any text described by the pattern.
With this powerful tool you can easily find all e-mail addresses, URLs, phone numbers, zip-codes, capitalized words, punctuation characters, dates, etc. Possibilities are only limited by your imagination!
- Built-in Regular Expressions editor with color syntax highlighting, contextual tooltips, and drag & drop
- RegEx toolbar that makes it easy to insert various RegEx elements and predefined patterns
- Use RegEx substitutions so you can include original matches or sub-matches in replacement pattern. This allows you to, for example, swap two pieces of text:
First, SecondSecond, First - 6 Built-in RegEx tools to help you design RegEx patterns: number selector, tag selector, line selector, etc.
- All major RegEx options supported: Multiline
m, Single lines, Ignore casei, Ignore pattern whitespacex, explicit capturen, ECMA Script, Right to Left, Culture-Invariant.
Replacement Text Style & Formatting
You can replace not only text content but also all the formatting too. Every formatting setting is optional, so you can fine-tune text format by for example specifying that you only want to change font color and everything else should remain as it was in original text.
- Font and Font Size
- Font Style: bold, italic, underline, strike-through
- Text Color
- Underline line style and color
- Superscript / Subscript
- Capitalization
- Highlight style
- Effects like Shadow and Outline
Insert New Content to Documents
Add / Insert New Content to Documents
You can insert new paragraphs into your documents easily. Paragraphs can be inserted at the beginning or at the end of a document.
Pro Tip You can insert text at arbitrary place(s) in the document using RegEx Replace action described above. This works by first finding the text before / after which you want to insert new content, and then specifying the replacement text so that it includes both the found / reference text as is (via $& RegEx match substitution) and the text to be inserted in the desired order (reference text followed by new text or vice-versa).
- Insert / append new content.
- Specify number of times new text be inserted (repeated).
- Optionally specify formatting for the new text. If formatting is not specified, original formatting will be used as is defined at the insertion point.
Delete Text & Remove Content from Documents
Remove All Matching Text from Documents
You can easily remove undesired text from your documents.
There are 3 ways in which you can specify which text should be removed:
- By Content - remove text by specifying a RegEx pattern that should match all occurrences of the text to be removed.
- By Location - remove text in specific paragraphs and / or document parts like headers and footers.
- By Formatting - remove text that has specific formatting.
You can combine all 3 ways to more precisely specify which text should be removed.
On The Screenshot All words beginning with capital A located in paragraphs 2 — 4 will be removed.
Remove Text Based on Formatting
You can also remove all text that has specific formatting. So you can target text for removal based not just on its location or content, but also formatting.
Only the selected formatting options will be checked and others will be ignored.
On The Screenshot All bold text will be removed.
Apply Formatting Styles to Text in Documents
Select Affected Text for which to Change Styles
You can easily change text styles and formatting in your documents. You first specify the affected text content, and then you specify new formatting by toggling the formatting options that should be set / changed like text color or font size.
There are 3 ways in which you can specify affected text:
- By Content - format text by specifying a RegEx pattern that should match all occurrences of the text whose style you want to change. For example, on the screenshot we are targeting all zip codes.
- By Location - format text in specific paragraphs and / or document parts like headers and footers.
- By Formatting - format text that has specific formatting. For example you may want to change all Red Text into Green Text.
You can combine all 3 ways to more precisely specify which text should be removed.
Specify New Font Style and Text Formatting Options
Specifying new text style and formatting is easy. Just put a checkmark next to a formatting / style setting you wish to change or set and select the desired value.
- Font and Font Size
- Font Style: bold, italic, underline, strike-through
- Text Color
- Underline line style and color
- Superscript / Subscript
- Capitalization
- Highlight style
- Effects like Shadow and Outline
Modify Document Properties & Meta-Data
You can change document properties and metadata in bulk.
For example, you can change the Author of a document or its Revision.
- Document Author / Last Modified By
- Title & Subject
- Description
- Keywords
- Version & Revision
- Created & Modified Date/Time (in addition to actual file attributes)
You can also remove all meta-data from documents.
Top Convenience Features
- 4 Processing Modes Manual, Automatic / Continuous, Triggered / Scheduled, Command Line.
- Conditional Processing lets you perform different operations with different files.
- Advanced File Naming and Renaming: use file properties, random characters, EXIF tags, perform search and replace.
- Advanced File Search: advanced wildcards, file properties, regular expressions, search in file contents.
- Extensive support for Regular Expressions (RegEx) throughout the program: file names, document contents, …
Hierarchical Action Sequence with Conditional Processing
Action Sequence
With Action Sequence you can easily specify which actions to perform on the selected files, under what circumstances, and in which order.
- Drag & drop to add, copy, and move actions
- Easily duplicate (copy) actions with all their settings
- Toggle individual actions on and off
- View a summary of action's settings right in the list
- Perform certain actions only when specified requirements are satisfied using conditions
- See condition relationships visually in a tree
- Save action sequence to XML-based template file
- Open / append previously saved action sequence
- Save action sequence summary to text file
- Get instant feedback about any errors
- See selected action details in tooltips
- Actions are numbered and color-coded to help you identify their order and distinguish different types of actions
You tell the program how to process files by adding various actions to the Action Sequence, which represents a sequence of operations to be performed step by step. In the Action Sequence, actions can be easily rearranged, moved around, duplicated using simple drag and drop operations and / or keyboard commands.
Conditions and Processing Paths
Conditional processing is possible with conditions, which are simply special actions that make sure that the actions that follow them should only be performed if particular requirements are satisfied: file name and file size match specified parameters, or a file contains certain text, etc. This results in potentially different processing paths for different files.
Actions and conditions are visually presented in the action sequence using numbered hierarchical tree-like list and arrows, making it easy to design and see processing logic and understand various relationships between the actions and conditions.
There is no limit to how many actions or conditions can be added to the action sequence, nor are there any restrictions as to how the actions should be ordered. Do whatever you need to accomplish your goals!
XML Templates
The action sequence that you design, including all the actions, conditions, levels of hierarchy, and individual action's settings can be easily saved to a file as XML-based template that you can reuse later. Because templates are XML-based, you can actually use any text editor or specialized XML tools to edit these templates afterwards. In addition, template files can be used for processing using command line and in Triggered / Scheduled Mode.
Processing Flow Branching and Conditional Processing with Conditions
Conditional processing allows you to perform different actions and operations on different documents. This is accomplished using Conditions in the actions sequence, which alter the processing flow, so that different documents may be processed using different processing paths!
Any actions that follow a condition in the action sequence will be performed only if the check(s) defined by the condition have been passed by the document being processed. Any actions nested inside a condition whose check(s) have not been passed by the documents will not be performed on those documents.
If another condition is encountered later, it may add to the effects of previously defined condition(s), so that any subsequent actions will be performed, provided the document being processed passes the new condition's check(s) as well.
- 8 Built-in conditions that can check document properties and content
- Conditions can be nested, which is equivalent to grouping conditions together using AND logical operator
- Conditions can be grouped together using either AND, OR (inclusive OR), or XOR (exclusive OR) logical operators
- Both the individual condition's check result as well as the check result of the whole condition group can be negated (logical NOT), which is useful when you want to apply certain actions to all documents except those matched by the condition(s)
- Nested conditions can have actions and/or layers between them to allow for complex hierarchical processing scenarios
- Condition relationships with each other as well as hierarchy of actions they control is clearly reflected in an action sequence with arrows and alignment, so you know which actions and layers are controlled by which condition(s)
File Information Condition
Check if the file being processed matches specified file properties such as name pattern, location, size, and attributes.
The following checks can be performed by this condition:
- File name and extension match a predefined pattern (either wildcards or RegEx)
- File's parent directory matches a predefined pattern (either wildcards or RegEx)
- File's full path matches a predefined pattern (RegEx only)
- File's size is within specified range: at least N bytes, at most N bytes, exactly N bytes, between N and M bytes, not equal to N bytes
- File's creation, change, and access dates are within specified range
- File's attributes match supplied values
Text Content Condition
Check if the document contains or does not contain specified text.
- 6 types of checks: contains, does not contain, start with, does not start with, ends with, does not end with
- Flexible contains check: contains at least N times, contains at most N times, contains exactly N times, contains between N and M times, contains but not N times.
- Support for wildcard character matching with *
- Case-insensitive search with Ignore Case option
- Support for RegEx-style character escapes: \x9E, \080, \u12AB
Condition Behavior Settings
Every condition has these common behavior settings that determine how it interacts with other conditions and thus how it affects document processing flow.
- Condition may allow further processing either if the requirements / check specified by it are met or not met (i.e. if the result of checking the document against a constraint is either True or False).
- Condition group behavior determines whether the conditions add to each other (i.e. each condition in a group adds additional requirements — equivalent to logical AND, or if the processing should continue as long as at least one condition in a group will pass — equivalent to logical OR.
- In addition it is possible to compare conditions inside a group using logical XOR operator, and negate the entire condition check.
- Negation of a condition or a condition group result may be very useful, because some times it is easier to define the checks for the True case and not for the negated case.
Manual Processing Mode
In Manual Mode you explicitly select documents for processing in a variety of ways. You can drag & drop documents from Windows Explorer; paste them from clipboard; add all documents from a given folder; add specific documents by selecting them from a list; search for specific documents that match given criteria; or paste file paths.
Additionally you can further refine the document list by unchecking the documents you wish to temporarily exclude from processing.
When satisfied with document selection, you can then manually process the whole batch. Processing can be started as long as the document list contains at least one checked document.
Manual Processing Mode
In Manual Mode the program processes documents only upon explicit initiation (when you add documents, and click on the Start button).
Documents can be added to the processing list in a variety of ways:
- Documents can be selected individually
- All documents from a particular folder can be added in one click
- Recursively scan directories and look for documents that match given criteria
- Drag and drop from Windows Explorer / Folder / Desktop
- Import from a text-based list of file paths
- Paste from clipboard
- Open from previously saved file list
- Directly from Windows by selecting documents in Windows Explorer, right-clicking, and launching the program that way (selected documents will be automatically added)
Processing in Manual Mode
When documents are processed in Manual Mode, a detailed progress is displayed right within the document list, letting you know which documenta are being processed and what is the processing stage
In addition, you can easily filter the document list by processing result status. For example, you may remove all successfully processed documents with just one click, leaving only those that had issues or were skipped.
- Add and remove documents easily
- Save document list for future use and append existing lists
- Temporarily prevent processing of certain documents by unchecking them
- Documents are color-coded after processing, making it easy to spot problems
- File path is intelligently drawn whereby file name stands out from the whole path, the start and the end of the file path are always visible
- An icon is displayed next to every file making it easier to identify file type
- Detailed tips appear when you hover over documents displaying file properties and even file's contents
- Processing result is displayed right within the document list with appropriate icon and a link to a detailed log
Automatic / Background / Continuous Processing Mode
In Automatic Mode, instead of selecting specific documents for processing, you setup "monitors" that tell the program which documents should be processed and when. The processing is performed automatically and continually when the specified conditions are met and the program is in the active monitoring mode.
A monitor works by performing periodic scans of the specified folder(s) for all the documents that match given criteria and satisfy monitor's behavior type (see below). All matching documents that were found by the monitor are then put into the processing queue. Periodicity of the scan/check can be controlled and can range anywhere from 1 minute to several hours or even days.
Depending on the monitor behavior type, document processing may be initiated under different conditions:
- File is Present - processing is performed on all documents matching criteria located the monitored folder (same document may be processed multiple times unless destination and original file paths differ and the original documents are deleted after processing).
- File was Modified - processing is performed on all documents that have been modified since the last time the monitored folder was checked.
- New File was Added - processing is performed only on the new documents that were added to the folder since the last time the folder was checked.
There is no limit to how many monitors you can setup — it only depends on the system resources that are available to you. The monitor setup can be easily saved to a template file for future use.
Once you have setup the monitors and actions, you can start monitoring and processing documents. Unlike the Manual Mode, processing in the Automatic Mode can be paused, so you can edit both the monitors and actions in the Action Sequence, and then safely resume processing.
Automatic Mode is ideal for cases when your workflow involves continually working with small batches of documents that are coming in periodically and require similar kind of processing.
3 Types of Monitors
The program supports 3 kinds of monitors: File Exists, File Added, and File Changed. Depending on the kind of monitor you setup, the processing will be triggered only when appropriate condition is met.
For example, if you set up a File Exists monitor, the program will always process all qualified documents in the monitored folder as long as they are present; however if you set up a File Added monitor, the program will process only the new documents that have been copied to or moved to the folder since the start of its monitoring.
How Monitors Work
The monitors work by continually scanning the specified folder (directory) and subfolders for specified documents that match a predefined naming pattern (mask) as well as other properties. The scanning happens at equally spaced time intervals that you define (refresh rate).
Among the file properties that may be examined are: file size, file dates, file attributes. Thus Batch Docs will enqueue for processing only those documents that match all the requirements specified in the monitor.
Monitors List
After a monitor has been set up, it will appear in the list of monitors.
You can define as many monitors as you like subject to the system resources you have and the product edition that you are using. Additionally, monitors can be enabled and disabled with a single click.
You can also save and open monitor lists easily, so you can reuse your monitor setups later.
Processing in Automatic Mode
In automatic mode processing works in 2 stages. First, the monitor(s) scan the specified folder(s) for any valid documents, and add them to the processing queue. Then the program automatically processes all the documents in that queue. These 2 stages need not be consecutive, as the program begins processing as soon as the queue is non-empty.
Unlike in the Manual Mode, in the Automatic Mode you can pause processing, make the changes to the actions in the actions sequence and / or the monitors, and then resume.
Triggered / Scheduled Processing Mode
Triggered or Scheduled Processing Mode lets you define different processing jobs that can be executed on schedule or a particular trigger, such as: on every Monday at 2:00; at Logon; on a particular system event; etc.
The program does not need to be running for the processing job to be activated - it will be automatically started with the right command line parameters at the right time by Windows Task Scheduler Service (which needs to be enabled for this feature to work) and begin performing the tasks defined by the processing job.
Processing jobs are easily managed within the program, but should the need arise, you can also modify their properties in Windows Task Scheduler directly.
Batch Docs can perform processing jobs in 3 different modes:
- Command Line Mode - only the console window will be displayed.
- GUI Mode - program is launched and performs processing displaying progress in regular Graphical User Interface.
- Invisible Mode - no user interface of any kind is shown, and the processing job is performed in the background.
All processing jobs can be different: for every job you can specify not only the trigger or schedule that will determine when it runs, but also the documents to be processed, actions to be performed, output file name pattern and directory, and a host of other options.
Triggered / Scheduled Processing Mode
In Triggered or Scheduled Processing Mode, document processing is started upon a specified event (trigger) or at a specific time as per the specified schedule.
You can create as many triggered/scheduled processing jobs as you want - all with different schedules, files to process, actions to perform, and other settings.
Batch Docs need not be running in order for the processing jobs to be activated, the program and processing is started automatically by Windows Task Scheduler Service.
Creating Processing Jobs
Creating a processing jobs is straight forward. You define some general settings such as job's name, mode of operation. Then you specify the job's schedule or trigger that will determine when the processing job is actually ran. Finally you specify the which documents should be processed; how the documents should be processed (which actions should be performed); and where the processed documents should be saved.
Managing Processing Jobs
Once the processing job has been created, it appears in the list of processing jobs. This list reflects all the jobs that have been created and are registered with Windows Task Scheduler Service which is responsible for job's execution.
Jobs can be enabled and disabled with a single click by putting or removing the checkmark next to the job's name in the list.
Saving Processed Documents
The following document formats are supported:
| Name | File Extension(s) | Read Support | Write Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Word Document | *.docx | ||
| Legacy Word Document | *.doc | ||
| Open Office Document | *.odt | ||
| Portable Document Format | |||
| XPS Document | *.xps | ||
| Rich Text Format | *.rtf | ||
| Web Page | *.htm, *.html | ||
| Plain Text File | *.txt | ||
| Wordpad Document | *.wpd |
Note Microsoft Word 2007 or later must be installed for the program to handle non-DocX formats! If Microsoft Word 2007 or later is not installed, the program will only be able to work with DocX documents.
Processed Documents: Destination Folder and File Name Options
Use Tags to Generate Dynamic File Names
There are close to 100 different tokens that can be used to generate dynamic file names that meet your requirements. Simply include the token in the appropriate place in the file name pattern to have dynamically generated content inserted in the right place (if the token generates content), or to affect the generated filename in other ways (if the token represents a command or operation).
The following tokens are available:
- File creation and modification dates, file size
- Document attributes and meta-data like author, title, etc.
- Current date and time
- Random numbers and letters
- File hashes: MD5, SHA1, SHA2, CRC…
- Original file name, extension, folder name
- Search & Replace operation letting you replace text within file name
- RegEx Replace - replace within file names using Regular Expressions
- Letter case modification commands (make upper case, lower case)
When it comes to saving processed documents, the program really shines, as it comes with built-in professional file renamer tool that lets you easily design file naming pattern simply by drag-dropping different name parts (tags) onto the text area. And there are many tags to choose from: various hashes and checksums like MD5, SHA, SHA2, CRC16, CRC32, etc; file size; parts of original name/folder; creation and modification dates and their parts; random characters; etc. You can even perform search and replace operations on the file name patterns you design!
Moreover the program can act solely as bulk file name renamer utility: you do not have to add any actions to the action sequence, and choose to only rename files instead!
Select Documents for Processing with Recursive File Search
Recursive Document Search
One of the ways you can add documents to the document list for processing is by doing a search for all documents that match criteria you specify. The program will scan selected directories and subdirectories for any valid documents and automatically add them to the list.
- Recursive scanning with customizable depth
- Specify files to include and exclude using highly customizable patterns and masks - much more powerful than your basic wildcards but easier to use than Regular Expressions!
- Specify directories to exclude from search
- Use Regular Expressions to specify file name patterns
- Use case sensitive matching
Note that you can save your customized document searches as templates for future use.
Search for Files Based on Properties
You can find documents you need for processing based on file properties like size or creation date, and attributes. This is in addition to basic search by name!
What's more is that you can fine tune these and select the exact ranges for all properties, like setting the size to be between 1MB and 5MB for example. With dates, too, you can be as specific as you want: you may, for example, look for files created on any day in May 2020, or on May 10 2020 specifically.
Search in Documents for Text Content
You can search for and add documents for processing using not just their names and properties, but actual contents as well. Perhaps you need to process only documents that start with a particular text; or only those documents that contain a particular phrase specified number of times. The program is very flexible!
Search for documents based on text content using these conditions:
- Contains at least N times
- Contains at most N times
- Contains exactly N times
- Contains between N and M times
- Does not Contain N times
- Does not Contain
- Starts with / Does Not Start with
- Ends with / Does Not End with
Ignore case option and wildcards are fully supported for more advanced searches!
In all of the processing modes, documents for processing can be selected using recursive (deep) document search, where the program automatically scans specified directories for documents matching desired criteria, such as: file name pattern, extension, size, dates, etc. This has several advantages:
- Program automatically searches for desired documents - no need to pick documents manually
- Not just file name and attributes, but also their textual content can be examined
- Complex searches can be saved and reused later
For finding documents with file names matching a specific pattern, you can either use extended wildcards with support for positive and negative matches, sub-masks, character ranges, grouping and alternation patterns; or use even more powerful Regular Expressions.
Triggered / Scheduled Processing Jobs
It is possible to create scheduled or triggered processing jobs that will be automatically performed even if the program is not running. And there is no limit to how many such jobs can be created!
For every job you can specify the documents to be processed, actions to be performed, output settings, and other processing options.
When the processing job is triggered, depending on the job's setting the program will be automatically launched in either GUI, console, or hidden mode, and the processing will be automatically started. When done, the program will exit automatically.
There are numerous triggers available: daily, weekly, monthly, event-based, etc.
Setup a Processing Job - General Properties
Processing jobs allow you to setup various batch document processing tasks that will be executed on a specified trigger or on schedule.
General properties include: name of the job, general timeframe when the job can be active, operation mode that determines if any UI will be shown, and user account together with security context under which the job will be executed.
Setup a Processing Job - Select Documents
There are several ways in which you can specify which documents should be processed by a processing job:
- Specified directories will be scanned for files matching a given name pattern
- Specified document search template will be used (see Recursive File Search)
- Specified list of files containing files' full paths will be used.
Setup a Processing Job - Specify Actions
Once you have specified which documents should be processed by a processing job, the next step is to specify how these documents should be processed, which actions and operations should be performed. This is done by specifying a previously saved Action Sequence.
Additionally you can customize a few other processing aspects like the number of processing threads and logging options.
Setup a Processing Job - Output Settings
Output settings determine where and how the processed documents are saved. All the options that are available in Step 3 in Manual and Automatic processing modes can be customized here as well. These include:
- File naming pattern and destination / output folder
- Document File Format and parameters
- Ability to define a third-party tool to execute after processing has finished
- Backup- and file saving- related options
Setup a Processing Job - Triggers
Last step in setting up a processing job is to define a trigger or specify a schedule that will determine when the processing job will actually execute.
The following triggers are available:
- Monthly - job executed on a monthly basis
- Weekly - job executed on a weekly basis
- Daily - job executed daily at a specified time or every specified time interval
- Event-Driven - job executed on a certain trigger like a given system event
Full Command Line Support & Console Operation
Batch Docs has full support for command line operation. It can not only be started from command line with specific options, but it can also run and operate entirely in console window.
A typical usage scenario would be to first specify a sequence of actions to be performed and then save that sequence to a template file. Then you can easily process files entirely from command line using a few switches: input directory and input file pattern, path to a saved action sequence template file, and output directory with file naming pattern.
Some benefits of command-line processing include:
- Ability to launch program and perform document processing on demand or by invoking it from third-party tools
- Perform processing a bit more efficiently without consuming a few extra resources needed to display and update Graphical User Interface
- Manually schedule the program to run with specific parameters using third-party scheduling programs or other automation software
- Execute batch processing tasks directly from Windows Power Shell
- Execution from a batch file with different parameters each time
- Simultaneous execution of several instances
- Faster startup and configuration as predefined command line snippets can be used, and in general typing is faster than manipulating UI elements
Other Features
Some other features that are not represented in the screenshots above:
- Can be integrated with Windows Explorer's right-click menu.
- Very detailed processing logging capabilities.
- Highly customizable with options and settings.
- Detailed tooltips throughout the whole program with intuitive UI guarantee fast learning curve!
- Fast multi-threaded processing that can utilize all available cores/CPUs.
- Run multiple program instances simultaneously.
- Multi-colored smart rendering of file paths in file lists that highlights most important parts of the file path, so that you can see file name, its parent directory as well as the drive - all at a glance.
- Program automatically remembers the values you enter into drop-down lists so that next time you need them, they can be selected from a drop-down! It also remembers the file paths you specify for documents and folders, so that if you ever reopen the same Select Folder or Choose Files dialog again, it will automatically be opened where you left it last time.
Customization & Extensibility
Although by itself Batch Docs is a professional product, it cannot possibly offer every feature you may want, or be used in all possible scenarios. This is not a problem however, because this product was built with extensibility in mind from the ground up.
The functionality offered by Batch Docs can be extended in the following ways:
- Software Development Kit (SDK) will let you develop your own actions and conditions that can be directly used by the product just as built-in ones. All that is required is basic knowledge of either C#, F#, or VB.NET and Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 / .NET Core 3.1 or higher.
- Actions Library will let you use all the various processing actions together with their UI in your own projects. Library is provided as a COM-Compatible .NET DLL that you can use in your own projects to leverage the functionality offered by the various processing actions.
- Custom Development - should you need it, we can customize the product for you so it specifically meets your needs. Batch Docs provides a solid foundation for batch file processing upon which our experienced developers can quickly create a customized, professional solution that meets your needs.
Software Development Kit (SDK)
You can easily extend functionality offered by Batch Docs' built-in actions by designing your own using this SDK as a guide. Batch Docs provides all the basic actions that perform general tasks, such as resize, crop, watermark, etc.; however you may have a need to process images in a specific way, and hence require custom actions.
With this SDK and basic VB.NET or C# programming skills you will be able to create your own custom actions that you can then use from within the program to effectively accomplish your goals. We recommend you use Microsoft's free Visual Studio Community to develop your extensions using this SDK, but of course if you have Visual Studio, SharpDevelop IDE, or any other IDE capable of producing .NET 3.5 libraries, you can use it as well.
Actions Library
Actions Library is provided as a COM-Compatible .NET DLL that you can use in your own projects to leverage the functionality offered by the product's various processing actions. Whereas with SDK you extend the product with the actions you create, with Actions Library you extend your own solution by utilizing the functionality of the product.
For example, if you want to use document processing capabilities offered by Batch Docs, with the Actions Library you will be able to do just that.
Actions Library needs to be acquired separately from the main product. So, please contact us to get Actions Library. We will also be happy to answer any questions you may have regarding licensing, pricing, integration, and other issues.
Let Us Customize Batch Docs for You!
If Batch Docs is not exactly what you are looking for, we can customize it for you so it specifically meets your needs! It can be done at a low cost to you, as Batch Docs provides a solid foundation upon which new features can be effectively added by our experienced developers to quickly create a customized, professional solution that meet your needs!
Keep in mind that contracting us to customize the product will be much cheaper and faster than hiring a programmer or doing the work with your own resources, as we have extensive experience in the area of custom development, and what's more - Batch Docs is a solid foundation upon which all the extra functionality that you desire can be built. Thousands of man-hours and over 100000's lines of code went into the creation of Batch Docs, so recreating even part of its functionality from scratch would require lots of resources.
Do you need customization?
- The product does not exactly meet your needs?
- Some feature you would like to use is not in the product?
- Would you like to add another action or operation?
- Need more options and customizations?
- Want to integrate the product with your existing business logic?
Custom Development Benefits
- No programming skills are required - we do everything for you!
- Low-cost professional development by experienced team
- Fast development because it leverages existing product and infrastructure
- Professional User Interface and familiarity as new features are integrated into existing product
- Royalty-free, flexible licensing model
Look no further! Contact us to request a quote and start custom development!